#02 | Load Data from APIs to a Pandas DataFrame in Python
Learn how to load data from APIs and convert them into ready-to-use DataFrames.

Photo by Ferenc Almasi on Unsplash
Table of contents
- Introduction
- The Uniform Resource Locator (URL)
- The API
- API's Data Response to Python
- Could you request the file from Python?
- How is the URL API Call related to the Data?
- What can we change to get the information about the Apple Stock (AAPL)?
- Why is not displaying the information of the Apple Stock? How can you solve the problem?
- Can we make plots and mathematical operations with the object data? Why?
- API's Data Response to a DataFrame
- Recap
- Other Example
© Jesús López 2022
Ask him any doubt on Twitter or LinkedIn
Introduction
The following image is pretty self-explanatory to understand how APIs work:
- The API is the waiter who
- Takes the request from the clients
- And take them to the kitchen
- To later serve the "cooked" response back to the clients

The Uniform Resource Locator (URL)
The URL is an address we use to locate files on the Internet:
- Documents: pdf, ppt, docx,...
- Multimedia: mp4, mp3, mov, png, jpeg,...
- Data Files: csv, json, db,...
Check out the following gif where we inspect the resources we download when locating economist.com.
URL - Watch Video

The API
An Application Program Interface (API) is a communications tool between the client and the server to carry out information through an URL.
The API defines the rules by which the URL will work. Like Python, the API contains:
- Functions
- Parameters
- Accepted Values
The only extra knowledge we need to consider is the use of tokens.
A token is a code you use in the request to validate your identity, as most platforms charge money to use their API.
Get a token from AlphaVantage and store it into a Python variable.
token = 'PASTE_YOUR_TOKEN_HERE'
Look for an API Call Example
In the website documentation.
'https://www.alphavantage.co/query?function=TIME_SERIES_INTRADAY&symbol=IBM&interval=5min&apikey=demo'
The API's Response
Every time you make a call to an API requesting some information, you later receive a response.
Check this JSON, a type of file that stores structured data returned by the API.
If you want to know more about the JSON file, see article.
The pattern:
- Base API:
https://www.alphavantage.co/query? - Parameters:
function=TIME_SERIES_INTRADAYsymbol=IBMinterval=5minapikey=demo
API's Data Response to Python
Could you request the file from Python?
import requests
api_call = 'https://www.alphavantage.co/query?function=TIME_SERIES_INTRADAY&symbol=IBM&interval=5min&apikey=demo'
requests.get(url=api_call)
>>> <Response [200]>
res = requests.get(url=api_call)
The function returns an object containing all the information related to the API request and response.
res.apparent_encoding
>>> 'ascii'
res.headers
>>> {'Date': 'Mon, 18 Jul 2022 18:01:19 GMT', 'Content-Type': 'application/json', 'Transfer-Encoding': 'chunked', 'Connection': 'keep-alive', 'Vary': 'Cookie', 'X-Frame-Options': 'SAMEORIGIN', 'Allow': 'GET, HEAD, OPTIONS', 'Via': '1.1 vegur', 'CF-Cache-Status': 'DYNAMIC', 'Expect-CT': 'max-age=604800, report-uri="https://report-uri.cloudflare.com/cdn-cgi/beacon/expect-ct"', 'Server': 'cloudflare', 'CF-RAY': '72cd1f3959323851-MAD', 'Content-Encoding': 'gzip'}
res.history
>>> []
To place the response object into a Python interpretable object, we need to use the function .json() to get a dictionary with the data.
res.json()
>>> {'Meta Data': {'1. Information': 'Intraday (5min) open, high, low, close prices and volume',
'2. Symbol': 'IBM',
'3. Last Refreshed': '2022-06-29 19:25:00',
'4. Interval': '5min',
'5. Output Size': 'Compact',
'6. Time Zone': 'US/Eastern'},
'Time Series (5min)': {'2022-06-29 19:25:00': {'1. open': '140.7100',
'2. high': '140.7100',
'3. low': '140.7100',
'4. close': '140.7100',
'5. volume': '531'},
...
'2022-06-28 17:25:00': {'1. open': '142.1500',
'2. high': '142.1500',
'3. low': '142.1500',
'4. close': '142.1500',
'5. volume': '100'}}}
data = res.json()
How is the URL API Call related to the Data?
The data in the dictionary represents the symbol IBM in intervals of 5min for the TIME_SERIES_INTRADAY.
Check the dictionary above to confirm.
res.request.path_url
>>> '/query?function=TIME_SERIES_INTRADAY&symbol=IBM&interval=5min&apikey=demo'
What can we change to get the information about the Apple Stock (AAPL)?
We need to change the value of the parameter symbol within the URL we use to call the API:
stock = 'AAPL'
api_call = f'https://www.alphavantage.co/query?function=TIME_SERIES_INTRADAY&symbol={stock}&interval=5min&apikey=demo'
res = requests.get(url=api_call)
res.json()
>>> {'Information': 'The **demo** API key is for demo purposes only. Please claim your free API key at (https://www.alphavantage.co/support/#api-key) to explore our full API offerings. It takes fewer than 20 seconds.'}
Why is not displaying the information of the Apple Stock? How can you solve the problem?
The API returns a JSON which implicitly says we previously used a *demo API key* to retrieve data from the symbol IBM. Nevertheless, using the same demo API key to retrieve the AAPL stock data is impossible.
We should include our token in the API call:
token
>>> 'YOUR_PASTED_TOKEN_ABOVE'
api_call = f'https://www.alphavantage.co/query?function=TIME_SERIES_INTRADAY&symbol={stock}&interval=5min&apikey={token}'
res = requests.get(url=api_call)
data = res.json()
data
>>> {'Meta Data': {'1. Information': 'Intraday (5min) open, high, low, close prices and volume',
'2. Symbol': 'AAPL',
'3. Last Refreshed': '2022-07-15 20:00:00',
'4. Interval': '5min',
'5. Output Size': 'Compact',
'6. Time Zone': 'US/Eastern'},
'Time Series (5min)': {'2022-06-29 19:25:00': {'1. open': '140.7100',
'2. high': '140.7100',
'3. low': '140.7100',
'4. close': '140.7100',
'5. volume': '531'},
...
'2022-06-28 17:25:00': {'1. open': '142.1500',
'2. high': '142.1500',
'3. low': '142.1500',
'4. close': '142.1500',
'5. volume': '100'}}}
Can we make plots and mathematical operations with the object data? Why?
data contains a dictionary, which it's a very simple Python object.
data.sum()
>>>
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
AttributeError Traceback (most recent call last)
Input In [46], in <cell line: 1>()
----> 1 data.sum()
AttributeError: 'dict' object has no attribute 'sum'
API's Data Response to a DataFrame
We need to create a DataFrame out of this dictionary to have a powerful object we could use to apply many functions.
import dataframe_image as dfi
import pandas as pd
pd.DataFrame(data=data)
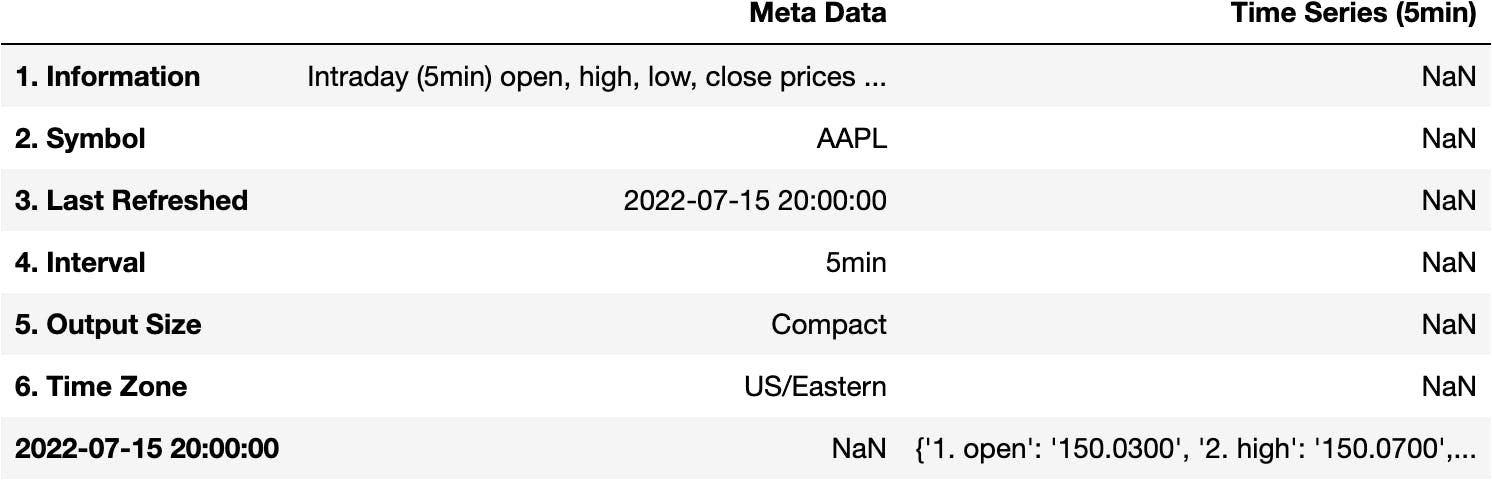
Filter the Information in the Response
We'd like to have the open, high, close,... variables as the columns. Not Meta Data and Time Series (5min). Why is this happening?
Meta DataandTime Series (5min)are thekeysof the dictionarydata.- The value of the key
Time Series (5min)key is the information we want in the DataFrame.
data['Time Series (5min)']
>>> {'2022-07-15 20:00:00': {'1. open': '150.0300',
'2. high': '150.0700',
'3. low': '150.0300',
'4. close': '150.0300',
'5. volume': '4752'},
...
'2022-06-28 17:25:00': {'1. open': '142.1500',
'2. high': '142.1500',
'3. low': '142.1500',
'4. close': '142.1500',
'5. volume': '100'}
pd.DataFrame(data['Time Series (5min)'])
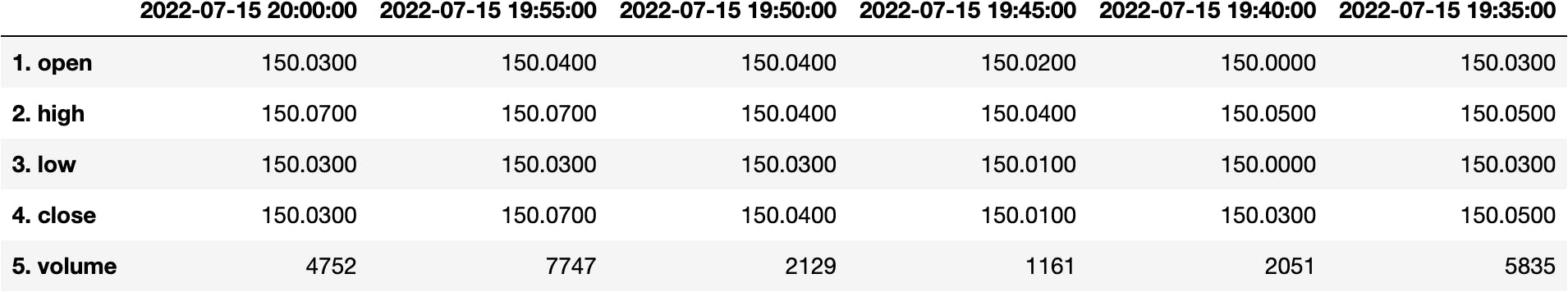
df_apple = pd.DataFrame(data['Time Series (5min)'])
Preprocess the DataFrame
The DataFrame is not represented as we'd like because the Dates are in the columns and the variables are in the index. So which function can we use to transpose the DataFrame?
df_apple.transpose()
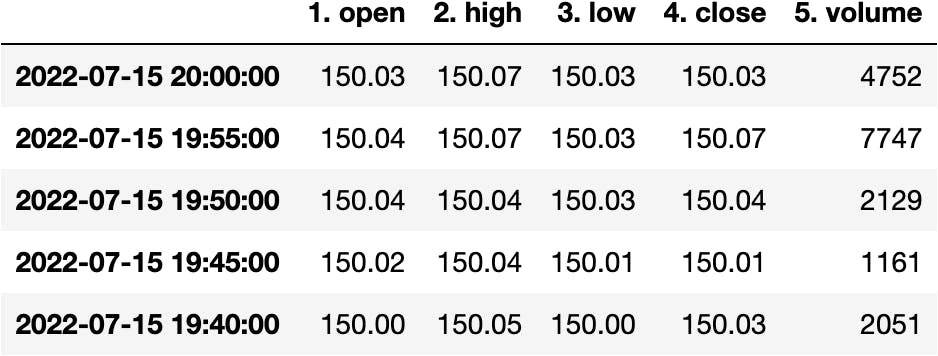
df_apple = df_apple.transpose()
Let's get the average value from the close price:
df_apple['4. close']
>>> 2022-07-15 20:00:00 150.0300
2022-07-15 19:55:00 150.0700
...
2022-07-15 11:45:00 149.1500
2022-07-15 11:40:00 149.1100
Name: 4. close, Length: 100, dtype: object
df_apple['4. close'].mean()
>>>
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
ValueError Traceback (most recent call last)
File ~/miniforge3/lib/python3.9/site-packages/pandas/core/nanops.py:1622, in _ensure_numeric(x)
1621 try:
-> 1622 x = float(x)
1623 except (TypeError, ValueError):
1624 # e.g. "1+1j" or "foo"
ValueError: could not convert string to float: '150.0300150.0700150.0400150.0100150.0300150.0500149.9900149.9900149.9800149.9900150.0000149.9900150.0000149.9900150.0000149.9800150.0000150.0100150.0500150.0100150.0100150.0000150.0200150.0100150.0100150.0098150.0100150.0000150.0200150.0000150.0007150.0100150.0100150.0200150.0325150.0200150.0300150.0200150.0000150.0300150.0001150.0000150.0000150.0100150.0560150.0500150.0900150.1700149.8900149.4410149.5300149.2700149.2160149.2094149.2000149.3450149.3778149.5450149.3600149.3500149.4700149.5400149.3993149.2150149.3015149.4100149.2916149.2650149.1200149.0400148.9800149.1350148.8800149.1850149.3924149.4600149.3496149.3250149.0874149.0600149.0000149.0101148.9350148.9100148.8620149.0050148.8100148.6340148.5500148.7600148.6950148.6800148.5488148.3500148.7351148.7910148.9305149.2000149.1500149.1100'
During handling of the above exception, another exception occurred:
ValueError Traceback (most recent call last)
File ~/miniforge3/lib/python3.9/site-packages/pandas/core/nanops.py:1626, in _ensure_numeric(x)
1625 try:
-> 1626 x = complex(x)
1627 except ValueError as err:
1628 # e.g. "foo"
ValueError: complex() arg is a malformed string
The above exception was the direct cause of the following exception:
TypeError Traceback (most recent call last)
Input In [38], in <cell line: 1>()
----> 1 df_apple['4. close'].mean()
File ~/miniforge3/lib/python3.9/site-packages/pandas/core/generic.py:11117, in NDFrame._add_numeric_operations.<locals>.mean(self, axis, skipna, level, numeric_only, **kwargs)
11099 @doc(
11100 _num_doc,
11101 desc="Return the mean of the values over the requested axis.",
(...)
11115 **kwargs,
11116 ):
> 11117 return NDFrame.mean(self, axis, skipna, level, numeric_only, **kwargs)
File ~/miniforge3/lib/python3.9/site-packages/pandas/core/generic.py:10687, in NDFrame.mean(self, axis, skipna, level, numeric_only, **kwargs)
10679 def mean(
10680 self,
10681 axis: Axis | None | lib.NoDefault = lib.no_default,
(...)
10685 **kwargs,
10686 ) -> Series | float:
> 10687 return self._stat_function(
10688 "mean", nanops.nanmean, axis, skipna, level, numeric_only, **kwargs
10689 )
File ~/miniforge3/lib/python3.9/site-packages/pandas/core/generic.py:10639, in NDFrame._stat_function(self, name, func, axis, skipna, level, numeric_only, **kwargs)
10629 warnings.warn(
10630 "Using the level keyword in DataFrame and Series aggregations is "
10631 "deprecated and will be removed in a future version. Use groupby "
(...)
10634 stacklevel=find_stack_level(),
10635 )
10636 return self._agg_by_level(
10637 name, axis=axis, level=level, skipna=skipna, numeric_only=numeric_only
10638 )
> 10639 return self._reduce(
10640 func, name=name, axis=axis, skipna=skipna, numeric_only=numeric_only
10641 )
File ~/miniforge3/lib/python3.9/site-packages/pandas/core/series.py:4471, in Series._reduce(self, op, name, axis, skipna, numeric_only, filter_type, **kwds)
4467 raise NotImplementedError(
4468 f"Series.{name} does not implement {kwd_name}."
4469 )
4470 with np.errstate(all="ignore"):
-> 4471 return op(delegate, skipna=skipna, **kwds)
File ~/miniforge3/lib/python3.9/site-packages/pandas/core/nanops.py:93, in disallow.__call__.<locals>._f(*args, **kwargs)
91 try:
92 with np.errstate(invalid="ignore"):
---> 93 return f(*args, **kwargs)
94 except ValueError as e:
95 # we want to transform an object array
96 # ValueError message to the more typical TypeError
97 # e.g. this is normally a disallowed function on
98 # object arrays that contain strings
99 if is_object_dtype(args[0]):
File ~/miniforge3/lib/python3.9/site-packages/pandas/core/nanops.py:155, in bottleneck_switch.__call__.<locals>.f(values, axis, skipna, **kwds)
153 result = alt(values, axis=axis, skipna=skipna, **kwds)
154 else:
--> 155 result = alt(values, axis=axis, skipna=skipna, **kwds)
157 return result
File ~/miniforge3/lib/python3.9/site-packages/pandas/core/nanops.py:410, in _datetimelike_compat.<locals>.new_func(values, axis, skipna, mask, **kwargs)
407 if datetimelike and mask is None:
408 mask = isna(values)
--> 410 result = func(values, axis=axis, skipna=skipna, mask=mask, **kwargs)
412 if datetimelike:
413 result = _wrap_results(result, orig_values.dtype, fill_value=iNaT)
File ~/miniforge3/lib/python3.9/site-packages/pandas/core/nanops.py:698, in nanmean(values, axis, skipna, mask)
695 dtype_count = dtype
697 count = _get_counts(values.shape, mask, axis, dtype=dtype_count)
--> 698 the_sum = _ensure_numeric(values.sum(axis, dtype=dtype_sum))
700 if axis is not None and getattr(the_sum, "ndim", False):
701 count = cast(np.ndarray, count)
File ~/miniforge3/lib/python3.9/site-packages/pandas/core/nanops.py:1629, in _ensure_numeric(x)
1626 x = complex(x)
1627 except ValueError as err:
1628 # e.g. "foo"
-> 1629 raise TypeError(f"Could not convert {x} to numeric") from err
1630 return x
TypeError: Could not convert 150.0300150.0700150.0400150.0100150.0300150.0500149.9900149.9900149.9800149.9900150.0000149.9900150.0000149.9900150.0000149.9800150.0000150.0100150.0500150.0100150.0100150.0000150.0200150.0100150.0100150.0098150.0100150.0000150.0200150.0000150.0007150.0100150.0100150.0200150.0325150.0200150.0300150.0200150.0000150.0300150.0001150.0000150.0000150.0100150.0560150.0500150.0900150.1700149.8900149.4410149.5300149.2700149.2160149.2094149.2000149.3450149.3778149.5450149.3600149.3500149.4700149.5400149.3993149.2150149.3015149.4100149.2916149.2650149.1200149.0400148.9800149.1350148.8800149.1850149.3924149.4600149.3496149.3250149.0874149.0600149.0000149.0101148.9350148.9100148.8620149.0050148.8100148.6340148.5500148.7600148.6950148.6800148.5488148.3500148.7351148.7910148.9305149.2000149.1500149.1100 to numeric
Why are we getting this ugly error?
- The values of the
Seriesaren't numerical objects.
df_apple.dtypes
>>> 1. open object
2. high object
3. low object
4. close object
5. volume object
dtype: object
Can you change the type of the values into numerical objects?
df_apple = df_apple.apply(pd.to_numeric)
Now that we have the Series values as numerical objects:
df_apple.dtypes
>>> 1. open float64
2. high float64
3. low float64
4. close float64
5. volume int64
dtype: object
We should be able to get the average close price:
df_apple['4. close'].mean()
>>> 149.551566
What else could we do?
df_apple.hist();
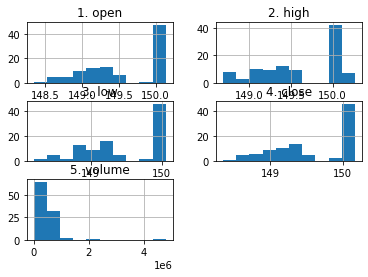
df_apple.hist(layout=(2,3), figsize=(15,8));
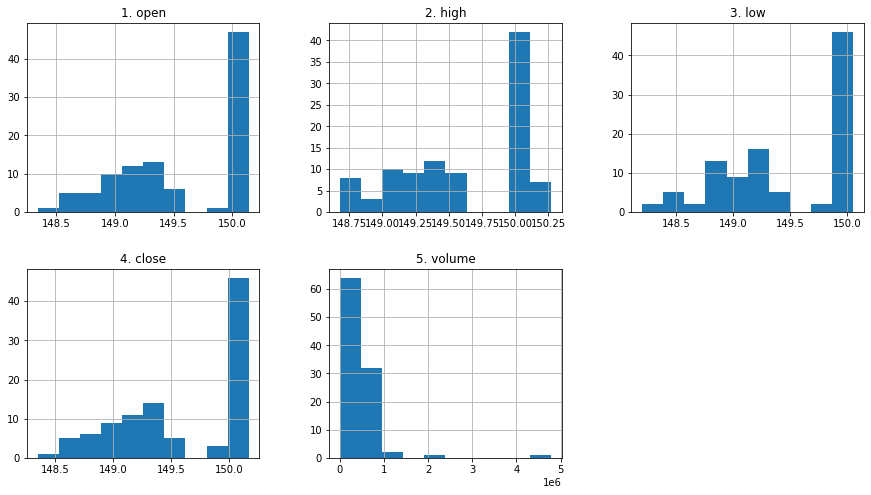
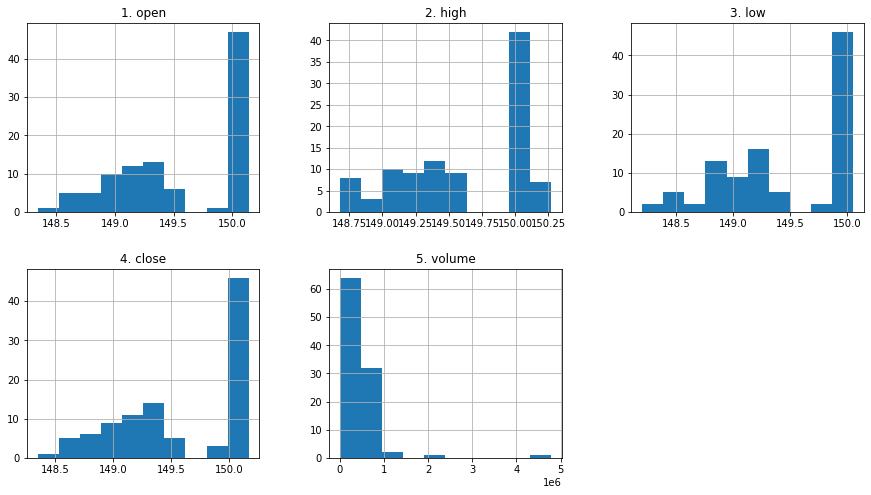
Recap
token = 'PASTE_YOUR_TOKEN_HERE'
stock = 'AAPL'
api_call = f'https://www.alphavantage.co/query?function=TIME_SERIES_INTRADAY&symbol={stock}&interval=5min&apikey={token}'
res = requests.get(url=api_call)
data = res.json()
df_apple = pd.DataFrame(data=data['Time Series (5min)'])
df_apple = df_apple.transpose()
df_apple = df_apple.apply(pd.to_numeric)
df_apple.hist(layout=(2,3), figsize=(15,8));
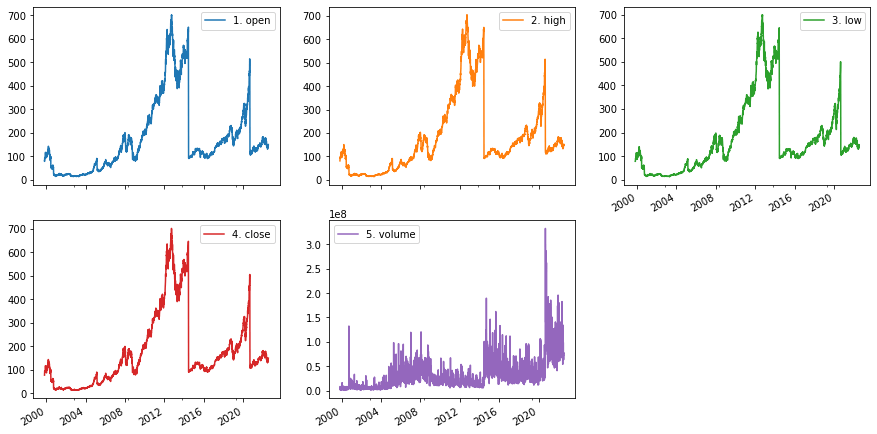
Other Example
size='full'
info_type = 'TIME_SERIES_DAILY'
api_call = f'https://www.alphavantage.co/query?function={info_type}&symbol={stock}&outputsize={size}&apikey={token}'
res = requests.get(url=api_call)
data = res.json()
df_apple_daily = pd.DataFrame(data['Time Series (Daily)'])
df_apple_daily = df_apple_daily.transpose()
df_apple_daily = df_apple_daily.apply(pd.to_numeric)
df_apple_daily.index = pd.to_datetime(df_apple_daily.index)
df_apple_daily.plot.line(layout=(2,3), figsize=(15,8), subplots=True);

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
